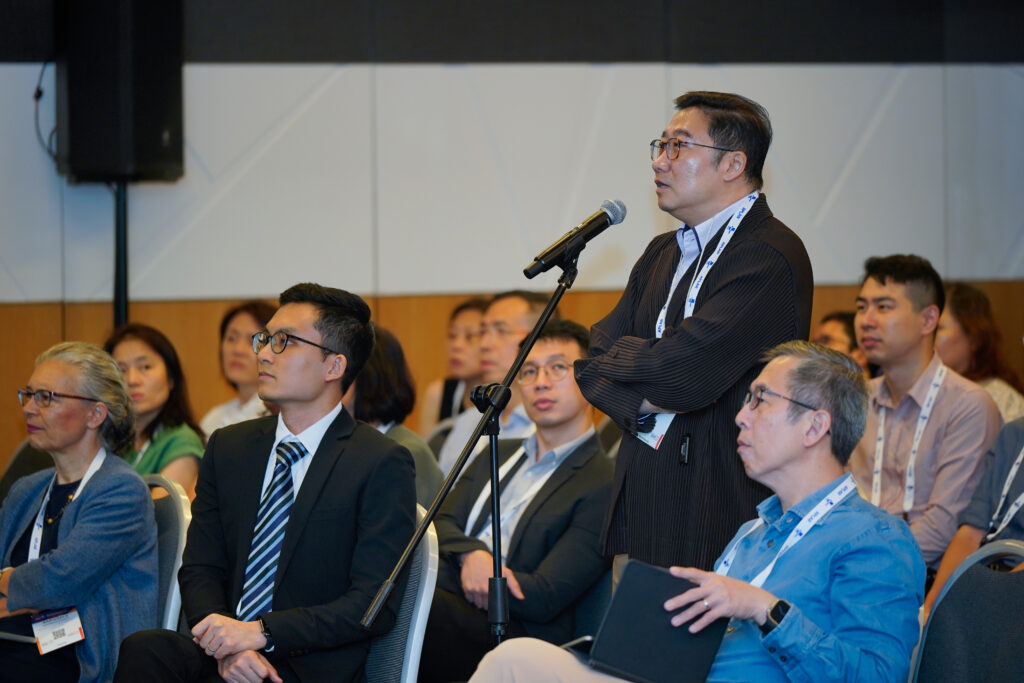
MSK Ultrasound workshop day 1
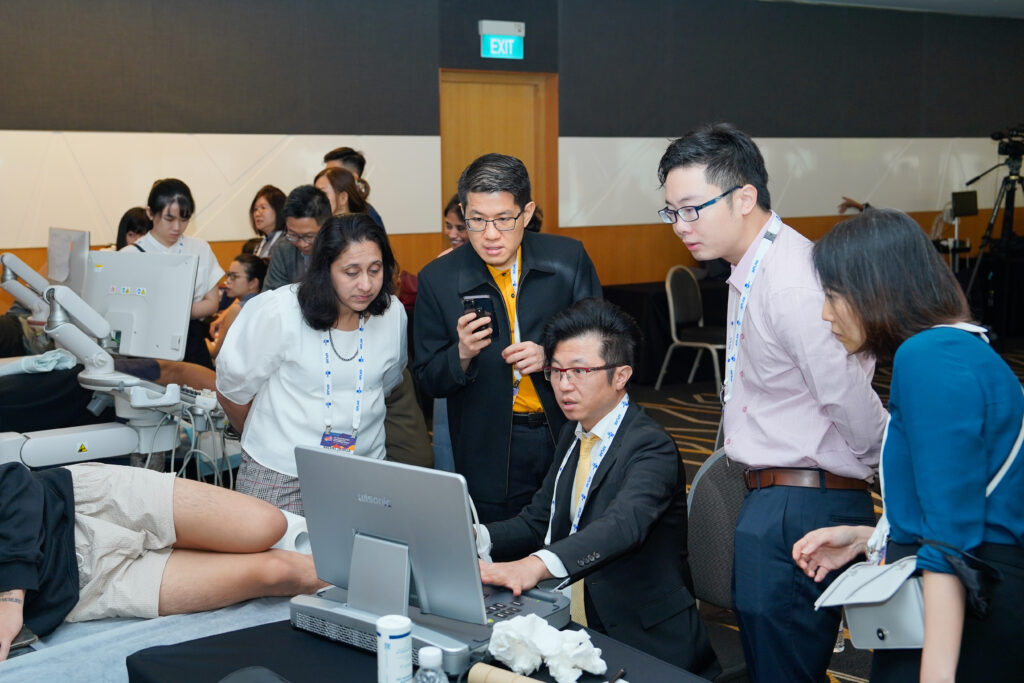
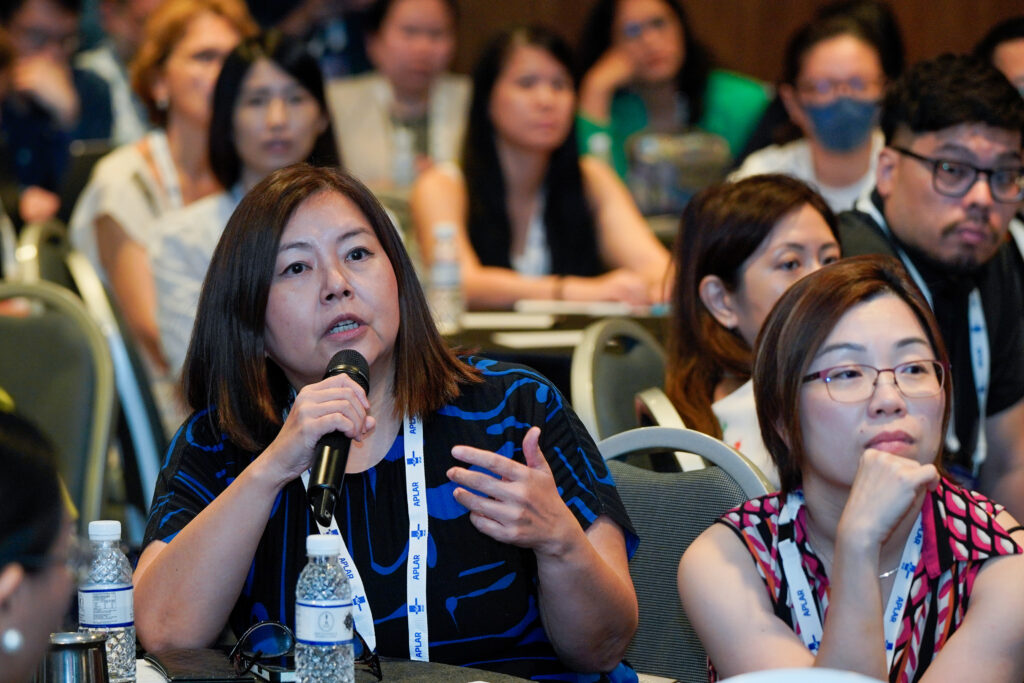
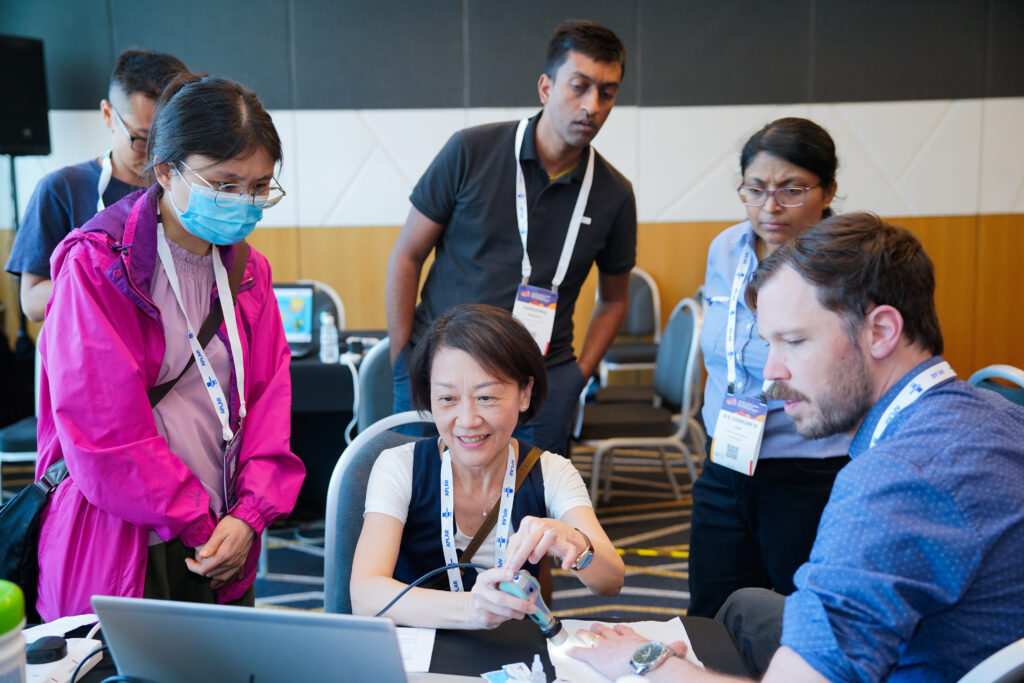
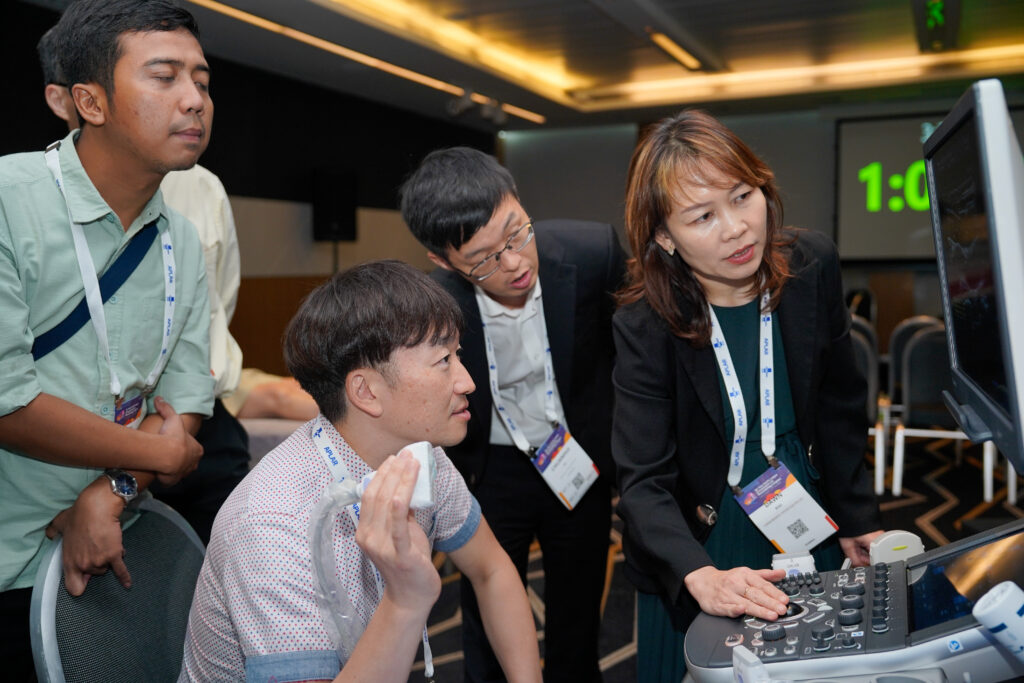




MSK Ultrasound Workshop Day 2


GRAPPA Symposium


Lupus Workshop sponsored by Lupus Academy


Crystal arthritis session: Keypoints
Reported by Dr Binit Vaidya
- Target serum urate level 5mg/dL
- Very slow serum urate targets may be harmful
- start low go slow strategy for urate lowering therapy might avoid the need of prophylaxis.
- Once target SUA achieved, there still might be lag in flare reduction.
- Febuxostat use achieved target UA similar to allopurinol but needed fewer dose adjustments and less rashes but at the cost of higher flare rates
- SGLTZ use was associated with 38% reduction in risk of gout flare

Challenges in diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis keypoints:

- Steroid masked rheumatoid arthritis can be difficult to diagnose.
- Acute phase reactants like ESR and CRP can be normal in 30-40% of cases.
- Elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis can present as polymyalgia rheumatica. MSUS high to be able to differentiate.
- 10-12% of monoarthritis may evolve to RA
- Interstitial lung disease might precede symptoms of RA in 4% of cases.
Managing RA in pregnancy Keypoints:
- Time to pregnancy us longer in RA patients than normal population. Higher prevalence of sub-fertility is reported in RA patients.
- Biological drugs might reduce time to pregnancy in RA.
- Disease activity improves in pregnancy with combined improved rate up to 60%.
- Postpartum flare seen in more than 40% of cases
- disease activity rather than treatment has been shown to increase the risk of adverse fetal outcomes.
- Teratogenic drugs are Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate, Mycophenolate. Insufficient data on Leflunomide.
- HCQ, SSZ, AZA, cyclosporin, tacrolimus are considered safe in pregnancy
- MTX should be stopped at least 1 month before pregnancy.
- LEF should be stopped 3.5 months before pregnancy
- JAKi recommended to be stopped 1 month before pregnancy (insufficient data)






Critical challenges and solutions in osteoporosis
Reported by Prof Kenneth Saag
Key points:
- No benefit of vitamin Desupplementation in preventing fractures-VITAL study.
- High dose supplement decreased bone density further.
- Calcium and Vitamin D(400 IU) lowers cancer
mortality but increased cardiovascular risk-an extension of Women Health Initiative study. - Bisphosphonate drug holiday can be tried in
those with low risk and improved BMD Tscore >-2.5. - Singledosezolindronicacid5mgisshownto maintain BMP for up to 6years. Yearly dosing
might not be needed in low risk patients. - Denosumab discontinuation rebounds the risk of Op fractures and increases risk of multiple
fractures. Adding bisphosphonates after denosumab reduces the risk of rebound. single dose of zolindronic acid after denosumab has
beneficial effects on BMP for up to 5 years. - Teriparatide has more beneficial effect in trabecular bone than cortical bone. Response to
triparatide and its differential effects in bone and spine varies genotypically. - Testosterone therapy for bone health only is not currently recommended.
Next revolution therapeutics of inflammatory arthritis:

keypoints:
- Ultrasound predicts progression to inflammatory arthritis.
- Extensor tenosynovitis is increasingly being recognized as high risk for progression.
- EULARhasgivendefinitionofclincially suspicious arthralgia in 2017 to assess risk of
persistence/ progression. - Abatacept has shown beneficial effects in
intercepting RA in pre-RAstage with improvements in composite outcome measures including reduction in MsUS detected subclincial inflammation. - Single dose rituximab, intermittent methotrexatetherapy, Hydroxychloroquine monotherapy interception studies have not
shown significant benefit.
Imaging in Crystal Arthropathies:

Key points:
- Allopurinol failure should be differentiated from post-treatment flares which is an expected phenomenon.
- Serum oxypurinol measurement can indicate real allopurinol failure.
- Wide dose variation and frequent dose escalations/adjustments make allopurinol use a hard work.
- Non-adherence, irregular prescribing, poorly resourced health systems are major contributors to allopurinol failure.
- Dose prediction based on ethnicity, body weight and renal function is being evaluated to reduce allopurinol failure.
Key points:
- MSUS has good sensitivity and specificity to detect crystals like uric acid and CPPD: intraarticular and periarticular.
- In gout MSUS findings are categorised as: double contour, aggregates and tophi.
- OMERACT group has defined grades of each MSUS finding in gout
- MSUS also has shown sensitivity to change demonstrating resolution of double countor and regression of aggregates and tophi temporally with treatment.
- MDCT can demonstrate exact crystal load/ volume.

Information coming soon.
Title
Reported by Prof John Doe
- Item
- Item
- Item
- Item
- Item

Title
Reported by Prof John Doe
- Item
- Item
- Item
- Item
- Item
